- 本文目录导读:
- Sweating and Detoxification
- The Physical Strain of High Temperatures
- Respiratory Issues
- Impact on Skin Health
- Potential for Overuse and Addiction
- Specific Risks for Certain Populations
- Guidelines for Safe Sauna Use
- Conclusion
Sweating and Detoxification
Sweating is a natural bodily function primarily designed to regulate body temperature. When we sweat, our bodies release fluids through our skin's sweat glands. This process not only cools the body but also helps eliminate some toxins. Sauna therapy, which includes both traditional steam saunas and modern infrared saunas, is often touted as a way to promote this natural detoxification process. The heat in the sauna causes the body to sweat profusely, which is believed to flush out impurities. However, while the benefits of sweating are well-documented, there are potential risks associated with excessive sweating and sauna use that should not be overlooked.
The Physical Strain of High Temperatures
Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, such as those found in saunas, can put significant strain on the cardiovascular system. When the body is subjected to intense heat, the heart has to work harder to pump blood to the skin's surface to facilitate cooling through sweating. This increased heart rate and blood flow can be particularly risky for individuals with pre-existing heart conditions or those who are otherwise not in peak physical health.
Moreover, excessive sweating can lead to dehydration if fluids are not adequately replenished. Dehydration can cause a variety of symptoms, including dizziness, headache, and in severe cases, heatstroke. The loss of electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, through sweat can also disrupt the body's normal physiological functions, leading to muscle cramps and weakness.
Respiratory Issues
The high humidity and heat of traditional steam saunas can exacerbate respiratory issues, particularly for individuals with asthma or other chronic respiratory conditions. The moist air can make breathing more difficult and trigger asthma attacks or other respiratory distress. On the other hand, infrared saunas, which do not rely on high humidity, may be less likely to cause such problems. However, they still expose users to intense heat, which can have similar cardiovascular and dehydration risks.
Impact on Skin Health
While sweating can help clear out pores and potentially improve skin health, excessive heat exposure can have the opposite effect. Prolonged sauna sessions can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation. Individuals with sensitive skin or conditions such as eczema may find that their symptoms worsen with frequent sauna use.
Additionally, the heat can cause the skin's capillaries to expand, which might lead to temporary redness or, in some cases, permanent damage such as broken capillaries. People prone to rosacea should be particularly cautious, as the heat can trigger flare-ups.

Potential for Overuse and Addiction
Like many wellness practices, sauna therapy can become addictive. The endorphin release and the feeling of relaxation post-session can lead to an over-reliance on sauna use as a form of stress relief. This overuse can exacerbate the physical risks mentioned above, particularly dehydration and cardiovascular strain.
It's important to practice moderation and to listen to one's body. Overusing saunas in an attempt to achieve greater detoxification or relaxation can lead to negative health outcomes rather than the intended benefits.
Specific Risks for Certain Populations
Certain populations should be particularly cautious when considering sauna therapy. Pregnant women, for example, are often advised to avoid high heat exposure as it can increase the risk of complications such as dehydration, overheating, and potentially affecting the developing fetus.
Similarly, individuals with kidney problems should be wary, as the dehydration associated with sauna use can exacerbate their condition. The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining the body's fluid balance, and excessive sweating can place additional strain on these organs.
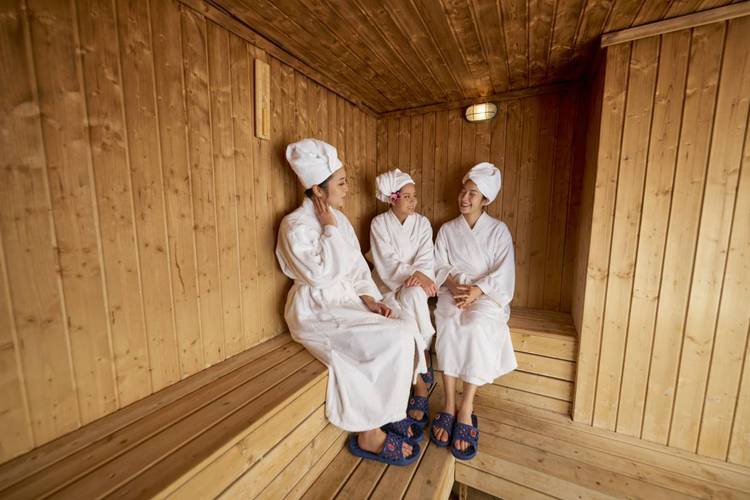

Guidelines for Safe Sauna Use
To mitigate the risks associated with sauna therapy, it's essential to follow some basic guidelines:
1. **Hydration**: Always drink plenty of water before and after a sauna session to compensate for the fluids lost through sweating.
2. **Duration**: Limit sauna sessions to 15-20 minutes. Prolonged exposure can increase the risk of dehydration and overheating.
3. **Listen to Your Body**: If you feel dizzy, lightheaded, or unwell, exit the sauna immediately and cool down gradually.

4. **Gradual Introduction**: If you are new to sauna use, start with shorter sessions and gradually increase the duration as your body adapts.
5. **Consultation**: Those with underlying health conditions should consult a healthcare professional before incorporating sauna therapy into their routine.
Conclusion
While sauna therapy offers several potential health benefits, including relaxation, improved circulation, and enhanced detoxification, it's crucial to approach it with caution. Understanding the risks, particularly those related to cardiovascular health, dehydration, respiratory issues, and skin conditions, can help users enjoy the benefits of sauna therapy without compromising their well-being. By following safe practices and listening to one's body, it is possible to integrate sauna sessions into a healthy lifestyle effectively.
转载请注明:成都会所桑拿-四川成都休闲桑拿推荐论坛! » 武汉休闲 » **The Hidden Dangers of Sauna Therapy: Understanding the Risks and Benefits**
版权声明
本文仅代表作者观点,不代表成都休闲网立场。
本文系作者授权发表,未经许可,不得转载。