In the realm of holistic health and wellness, traditional methods often find themselves juxtaposed against modern medical practices. One such tradition is sweating therapy, or "汗蒸" (han zheng) in Chinese, which involves the use of heat to induce sweating and promote health. This practice, rooted in ancient traditions, stands in contrast to the scientifically rigorous approach of Western medicine. In this article, we will explore the benefits of sweating therapy, compare it with the principles of Western medicine, and examine how both can be integrated for optimal health.
Sweating therapy has been practiced for centuries in various cultures. From the Finnish sauna to the Turkish hammam, the concept of using heat to cleanse the body and mind is universal. In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), sweating therapy is believed to stimulate the body's energy channels, improve circulation, and expel toxins. This practice is often seen as a way to balance the body's yin and yang, promoting overall well-being.
Western medicine, on the other hand, is based on scientific research and empirical evidence. It relies on a detailed understanding of human anatomy, physiology, and pathology. Treatments in Western medicine are often targeted and specific, designed to address particular health issues through medications, surgeries, and other interventions. While sweating therapy is holistic, focusing on the body as a whole, Western medicine tends to be more segmented, addressing individual symptoms or conditions.
Despite these differences, there are intersections where sweating therapy and Western medicine can complement each other. For instance, sweating therapy is known to improve cardiovascular health. The heat exposure leads to an increase in heart rate and sweating, which mimics the effects of moderate exercise. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who are unable to engage in physical activity due to various health conditions. Studies have shown that regular sauna use can lower blood pressure, improve arterial function, and reduce the risk of heart-related diseases. These findings align with Western medical principles that emphasize the importance of cardiovascular health.

Additionally, sweating therapy can aid in detoxification. While Western medicine recognizes the liver and kidneys as the primary organs responsible for detoxification, the skin is also an important organ for eliminating toxins. Sweating can help remove heavy metals, such as lead and mercury, from the body. This is particularly relevant in today's environment, where exposure to various pollutants is almost unavoidable. The process of sweating can thus support the body's natural detoxification mechanisms, a concept appreciated by both traditional and modern medical practices.
Another area where sweating therapy and Western medicine intersect is in the management of stress and mental health. The relaxing environment of a sauna or steam room can help reduce stress levels, improve mood, and promote relaxation. This is supported by research in Western medicine, which shows that relaxation techniques, including those that induce sweating, can reduce cortisol levels and improve mental well-being. In an age where stress-related conditions such as anxiety and depression are on the rise, integrating sweating therapy with conventional treatments can provide a holistic approach to mental health.
Pain management is another domain where sweating therapy can be beneficial. Heat therapy is a well-recognized method for alleviating muscle and joint pain in both traditional and Western medical practices. The warmth from sweating therapy can help relax muscles, reduce stiffness, and improve mobility. This makes it a useful complementary treatment for conditions like arthritis, fibromyalgia, and chronic pain syndromes. By enhancing blood flow and promoting relaxation, sweating therapy can help reduce pain and improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions.

It's also important to note the immune-boosting effects of sweating therapy. Regular sauna use has been linked to a reduced incidence of common colds and other infections. The heat exposure can stimulate the production of white blood cells, which are crucial for the immune response. This is in line with Western medicine's understanding of the immune system, where maintaining a strong immune defense is key to preventing and fighting infections.
While the benefits of sweating therapy are numerous, it is essential to approach it with caution, particularly for individuals with certain medical conditions. People with cardiovascular issues, respiratory problems, or those who are pregnant should consult with a healthcare professional before engaging in sweating therapy. Western medicine provides the necessary guidelines and precautions to ensure that such therapies are safe and beneficial.
In conclusion, sweating therapy and Western medicine, though originating from different paradigms, can complement each other in promoting health and wellness. Sweating therapy offers a holistic approach that emphasizes detoxification, relaxation, and overall balance, while Western medicine provides a targeted, evidence-based approach to treating specific conditions. By integrating the strengths of both, individuals can achieve a more comprehensive and effective approach to health.
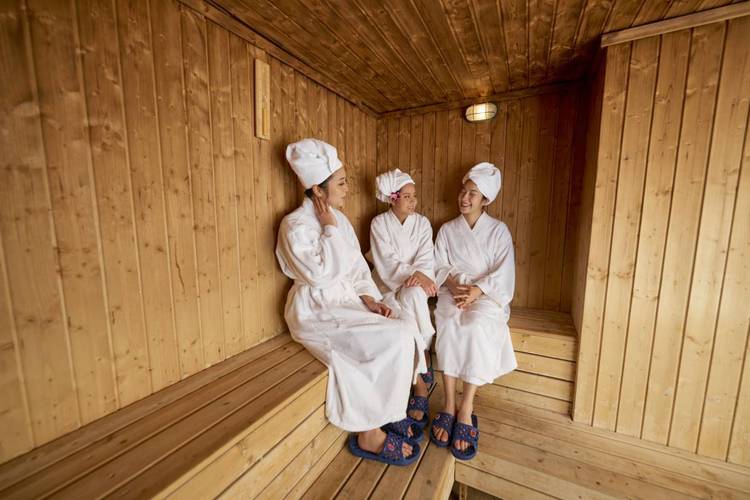

As the interest in holistic health continues to grow, it is important to recognize and respect the value of both traditional practices like sweating therapy and modern medical advancements. This integrated approach not only broadens our understanding of health but also provides a richer, more nuanced perspective on how to achieve and maintain wellness in today's complex world.
转载请注明:成都会所桑拿-四川成都休闲桑拿推荐论坛! » 武汉休闲 » Sweating Therapy vs. Western Medicine: An In-Depth Exploration of Health Benefits
版权声明
本文仅代表作者观点,不代表成都休闲网立场。
本文系作者授权发表,未经许可,不得转载。